C++的IO处理中的头文件以及类理解(2)<sstream>头文件
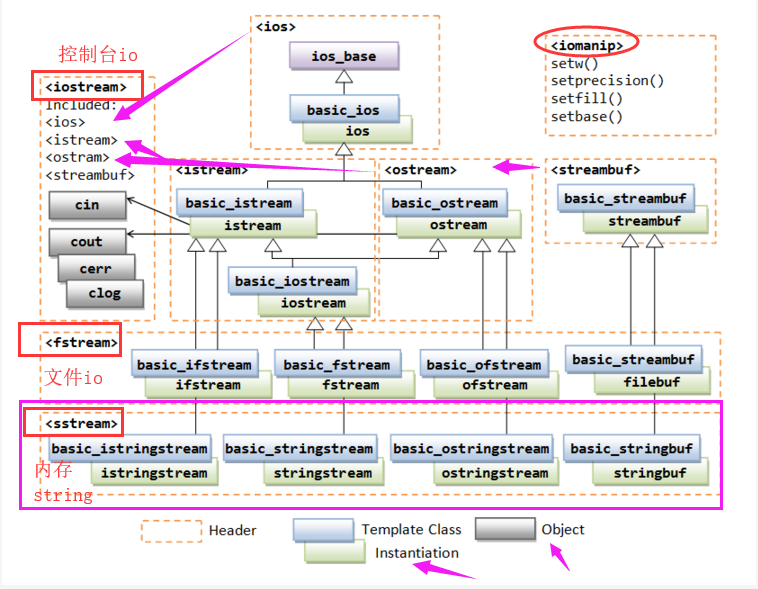
头文件<sstream>中定义的类型都继承iostream头文件中定义的类型。除了继承得来的操作,sstream中定义的类型还增加了一些成员来管理与流相关联的string.
一、 <sstream>头文件
该标准头文件中包含了ostringstream、istringstream、stringstream这三个类,要使用他们创建对象,对内存中的string对象进行io处理。
这些类型可以向string写入数据,从string读取数据,就像string是一个IO流一样。
istringstream从string读取数据,(istringstream对象用来把一个已定字符串中的以空格、Tab隔开的内容提取出来,功能类似于C语言中的sscanf函数)只支持>>操作符,
ostringstream向string写入数据,只支持<<操作符,stringstream既可从string读数据也可向string写数据,支持<<、>>操作符。
类:
1. stringbuf 类
构造一个string stream buffer (字符串流对象)。
构造函数如下:
default (1) initialization (2) copy (3) move (4)
(1)空的构造函数, 默认构造函数
构造一个 stringbuf 对象, 用一个空的序列, 参数which是 设置的open model。
(2)初始化构造函数
用一个string 对象作为内容,来构造stringbuf 对象, 参数which 是打开模式
(3)拷贝构造函数
应为已经deleted,舍弃,因此没有拷贝构造。
(4)移动构造函数
获取参数stringbuf x 的内容;
x 处于不确定但是有效的状态。
不确定内部的sequence 是x ,或者是x 的拷贝, 但是两个都是相关依赖的序列。
参数情况:
str, 参数string对象,内容已经拷贝;
x, 参数stringbuf对象,其内容已经移动;
which:打开输出xx对象的模式, 即进入内部stringbuf对象,给定的字符串序列。 是一个枚举类型。任意合并值都是重要影响。
- os_base::in, 表示:input, 内部的字符串序列支持input 操作;
- ios_base::out: 表示,output, 序列支持输出操作。
- ios_base::ate:表示 at end, 写入位置在构造函数的后面, 并且在每次用str()成员重置内容后。
- 其他类型的ios_base::openmode, 例如: ios_base::app. 注意, ios_base::out ,总是设置ostringsteam 对象, 尽管没有显示设置参数which。 注意, ostringsteam是一个输出steam, 其内部的stringbuf对象可能设置支持input 操作的。
测试程序:
// stringbuf example#include// std::cout, std::ostream, std::hex#include // std::stringbuf#include // std::stringint main (){ std::stringbuf buffer; // empty stringbuf //将 stringbuf 对象与 输出流关联,这样,可以利用输出输入,对stringbuf对象进行赋值。 std::ostream os (&buffer); // associate stream buffer to stream // mixing output to buffer with inserting to associated stream: //函数sputn(),
buffer.sputn ("255 in hexadecimal: ",20); os << std::hex << 255; std::cout << buffer.str();// 拷贝当前stringbuf 对象内内容,并以string对象返回。 return 0;} 输出
255 in hexadecimal: ff
注意:
::sputn()函数原型
streamsize sputn (const char* s, streamsize n); 作用: 将字符序列写入到streambuf内部的内容中。 参数: s:指向字符串序列的指针,用于将要写入stringbuf的内容。 n:将要写入字符的长度, 非负值, streamsize是符号整数类型。 返回: 已经写入字符的数量// sputn() example#include// std::streambuf#include // std::ofstreamint main () { //字符序列,字符数组,指针 const char sentence[]= "Sample sentence";//注意,末尾有字符串终止符号1个字符 std::ofstream ostr ("test.txt"); if (ostr) { std::streambuf * pbuf = ostr.rdbuf(); //直接用streambuf进行直接输入内容 pbuf->sputn (sentence,sizeof(sentence)-1); ostr.close(); } return 0;}
2. . 测试
::ostringstream()构造函数
测试:
// ostringstream constructor#include// std::cout, std::ios#include // std::ostringstreamint main () { std::ostringstream foo; // out std::ostringstream bar (std::ostringstream::ate); // out|ate foo.str("Test string"); bar.str("Test string"); foo << 101; bar << 101; std::cout << foo.str() << '\n'; std::cout << bar.str() << '\n'; return 0;} 输出:
101t string
Test string101
ostringstream, istringstream,stringstream类型的用法程序
#include "sstream.hpp"#include#include // ostringstream/istringstream/stringstream#include // reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/sstream/ostringstream/int test_ostringstream(){ // ostringstream: Output stream class to operate on strings // 1. rdbuf: Returns a pointer to the internal stringbuf object std::ostringstream oss1; // using stringbuf directly 直接使用内部的stringbuf来进行输出,用函数 std::stringbuf *pbuf = oss1.rdbuf(); pbuf->sputn("Sample string", 13);//输入字符个数13的一个字符数组。 std::cout << pbuf->str() << std::endl;//获取输出内容的字符串形式 // 2. str(): 返回当前strem对象内的内容拷贝的数据,以字符串返回。returns a string object with a copy of the current contents of the stream // str(const string& s): 删除string对象之前的内容, 并设置为与steam对象内的内容一样的数据。sets s as the contents of the stream, discarding any previous contents. // The object preserves its open mode: if this includes ios_base::ate,注意,如果包含ios_base::ate模式,则对象讲标六之前的内容, 写入的位置将会移动到new sequence的末尾。 // the writing position is moved to the end of the new sequence std::ostringstream oss2; oss2 << "One hundred and one: " << 101; std::string s1 = oss2.str(); std::cout << s1 << '\n'; // 3. swap: c++11, Exchanges all internal data between x and *this // 将参数ostringsteam 的内用与当前ostringsteam内容互换。 std::ostringstream foo; std::ostringstream bar; foo << 100; bar << 200; foo.swap(bar); std::cout << "foo: " << foo.str() << '\n'; std::cout << "bar: " << bar.str() << '\n'; // 4. swap: Exchanges the values of the ostringstream objects x and y std::ostringstream foo2; std::ostringstream bar2; foo2 << 100; bar2 << 200; std::swap(foo2, bar2); // unqualified (uses argument-dependent lookup) std::cout << "foo2: " << foo2.str() << '\n'; std::cout << "bar2: " << bar2.str() << '\n'; // 5. ostringstream constructor: Construct an object and optionally initialize its content // explicit ostringstream ( openmode which = ios_base::out ); // explicit ostringstream ( const string & str, openmode which = ios_base::out ); std::ostringstream foo3; // out, 默认的 std::ostringstream bar3(std::ostringstream::ate); // out|ate, 这是追加模式,任何后续的输入,到从streambuf的末尾追加。 foo3.str("Test string"); // str: sets s as the contents of the stream, discarding any previous contents bar3.str("Test string"); foo3 << 101; bar3 << 101; std::cout << foo3.str() << '\n'; // 101t string std::cout << bar3.str() << '\n'; // Test string101 std::string s{ "abcde" }; std::ostringstream foo4(s); // 创建存储s的副本的ostringstream对象 std::cout << "foo4: " << foo4.str() << std::endl; // reference: https://latedev.wordpress.com/2011/11/16/c-stringstreams/ std::ostringstream os; os << "the "; os << "quick "; os << "brown "; os << "fox"; std::string s2 = os.str(); std::cout << s2 << std::endl; // double to string ==> c++11 to_string double d = 123.45; std::ostringstream os3; os3 << d; std::string s3 = "The value of d is " + os3.str(); std::cout << s3 << std::endl; return 0;} // reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/sstream/istringstream/int test_istringstream(){ // istringstream: Input stream class to operate on strings 输入流类来操作string类型 // 1. istringstream constructor std::istringstream is("the quick brown fox"); std::string s; while (is >> s) { //直接用输入流来设置string std::cout << s << std::endl; } std::string stringvalues = "125 320 512 750 333"; std::istringstream iss6(stringvalues);//用字符串设置输入流 for (int n = 0; n<5; n++) { int val; // Elements in a character stream are considered to be separated by 'white space' // which is basically space, tab and newline characters,空格符,tab, 下一行的符号,都来表示分隔符 iss6 >> val; std::cout << val * 2 << '\n'; } // 2. rdbuf: Returns a pointer to the internal stringbuf object, with which the object was associated on construction //返回指针,指向内部的stringbuf对象, 这是早stringsteam流在创建的时候关联的。 std::istringstream iss; std::stringbuf *pbuf = iss.rdbuf(); // using stringbuf directly:直接用stringbuf作为输入,最终表现仍然是istringsteam对象 pbuf->str("Example string"); int size = pbuf->in_avail(); while (pbuf->in_avail()>0) std::cout << static_cast (pbuf->sbumpc()); std::cout << std::endl; // 3. str(): returns a string object with a copy of the current contents of the stream // str(const string& s): sets str as the contents of the stream, discarding any previous contents. // The object preserves its open mode: if this includes ios_base::ate, // the writing position is moved to the end of the new sequence std::istringstream iss2; std::string strvalues = "32 240 2 1450"; iss2.str(strvalues);//用参数stirng类设置istringsteam的内容。 for (int n = 0; n<4; n++) { int val; // Elements in a character stream are considered to be separated by 'white space' // which is basically space, tab and newline characters iss2 >> val;//依次输出到变量string std::cout << val << '\n'; } std::cout << "Finished writing the numbers in: "; std::cout << iss2.str() << '\n'; // 4. swap: c++11, Exchanges all internal data between x and *this. std::istringstream foo("100"); std::istringstream bar("200"); foo.swap(bar); int val; foo >> val; std::cout << "foo: " << val << '\n'; // 200 bar >> val; std::cout << "bar: " << val << '\n'; // 100 // 5. swap: Exchanges the values of the istringstream objects x and y std::istringstream foo2("100"); std::istringstream bar2("200"); swap(foo2, bar2); // unqualified (uses argument-dependent lookup) int val2; foo2 >> val2; std::cout << "foo2: " << val2<< '\n'; // 200 bar2 >> val2; std::cout << "bar2: " << val2 << '\n'; // 100 return 0;} // reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/sstream/stringstream/int test_stringstream(){ // 1. stringstream: Stream class to operate on strings std::stringstream ss;//即处理输入字符串,有处理输出字符串 ss << 100 << ' ' << 200; int foo, bar; ss >> foo >> bar; std::cout << "foo: " << foo << '\n'; // 100 std::cout << "bar: " << bar << '\n'; // 200 // 2. rdbuf: Returns a pointer to the internal stringbuf object, with which the object was associated on construction std::stringstream ss2; // using stringbuf directly: std::stringbuf *pbuf = ss2.rdbuf(); pbuf->sputn("Example string", 13);//输入 13个字符的字符串 char buffer[80]; pbuf->sgetn(buffer, 80);//获取80个字符的string buffer std::cout << buffer << std::endl; // 3. str(): returns a string object with a copy of the current contents of the stream // str(const string& s): sets s as the contents of the stream, discarding any previous contents. // The object preserves its open mode: if this includes ios_base::ate, // the writing position is moved to the end of the new sequence std::stringstream ss3; ss3.str("Example string");// str()函数作为内容输入 std::string s3 = ss3.str();//输出内部内容,以字符串形式 std::cout << s3 << '\n'; // 4.1 swap: c++11, Exchanges all internal data between x and *this std::stringstream foo4; std::stringstream bar4; foo4 << 100; bar4 << 200; foo4.swap(bar4); int val; foo4 >> val; std::cout << "foo4: " << val << '\n'; // 200 bar4 >> val; std::cout << "bar4: " << val << '\n'; // 100 // 4.2 swap(stringstream): Exchanges the values of the stringstream objects x and y std::stringstream foo5; std::stringstream bar5; foo5 << 100; bar5 << 200; std::swap(foo5, bar5); int val5; foo5 >> val5; std::cout << "foo5: " << val5 << '\n'; // 200 bar5 >> val5; std::cout << "bar5: " << val5 << '\n'; // 100 return 0;}
3. C++还提供了另一个头文件<strsteam>,其功能和<ssteam>相似,是为了兼容c 类型的字符串(字符数组)而提出来的。
<strstream> 中istrstream,ostrstream,strstream 也有对应的三个类型。
istrstream类用于执行C风格的串流的输入操作,也就是以字符数组作为输入设备。
ostrstream类用于执行C风格的串流的输出操作,也就是一字符数组作为输出设备。 strstream类同时可以支持C风格的串流的输入输出操作。
注意:
strstream里的东西已经被c++标准明确标明为“不要再使用”
endl;